Are you looking for a natural way to improve your garden’s soil quality?
Look no further than peat moss!
This incredible material is more than just a fluffy addition to your planting mix – it’s a powerful organic amendment that can supercharge your plants’ growth and health.
Whether you’re an experienced gardener or just starting out, peat moss is a must-have in your toolkit.
So come along as we explore the amazing world of this versatile and fascinating material!
What is peat moss?
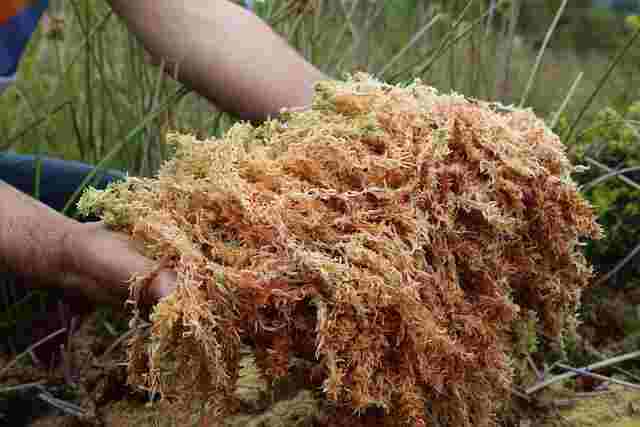

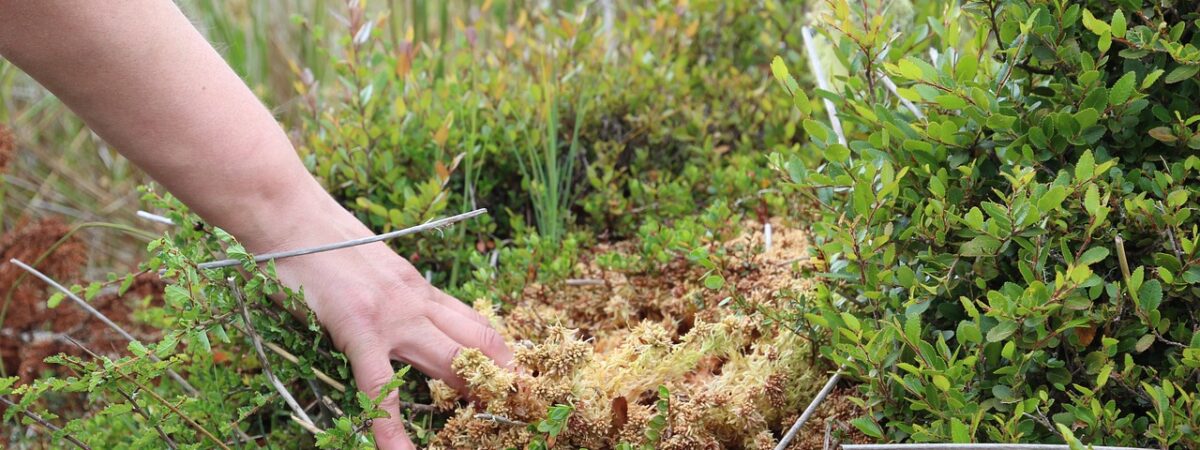
Peat moss is a type of organic matter that forms in wetlands and bogs. It is composed mainly of partially decomposed sphagnum moss and other plant materials that have accumulated over thousands of years. It is commonly used as a soil amendment in gardening and agriculture due to its ability to retain water and nutrients.
Peat moss is often used as a soil conditioner because of its high water-holding capacity. It can absorb and hold up to 20 times its weight in water, which can be useful in preventing soil from drying out too quickly.
Additionally, it has a low pH, which can help to acidify soil, making it ideal for plants that thrive in acidic environments, such as blueberries and rhododendrons.
Peat moss is also used as a component in potting mixes for plants. It provides a lightweight and porous structure to the mix, which allows for good drainage and aeration of the roots. It is also a source of organic matter, which can provide nutrients to plants as it decomposes.
However, the use of this is not without controversy. Harvesting peat moss from wetlands can have a negative impact on the environment by disrupting delicate ecosystems, releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, and contributing to the loss of biodiversity.
As a result, some gardeners and environmentalists choose to avoid the use of peat moss and instead use alternative soil amendments, such as compost or coconut coir.
Types of peat moss
There are several types of peat moss available, including:
Sphagnum Peat Moss
This is the most common type, harvested from sphagnum bogs. It has a high water-holding capacity, is acidic in nature, and is a good source of organic matter.
Reed-Sedge Peat Moss
This type is harvested from reed-sedge bogs. It has a lower water-holding capacity than sphagnum peat moss but is still a good source of organic matter.
Hypnum Peat Moss
This type is harvested from hypnum bogs. It has a lower water-holding capacity than sphagnum peat moss and is less acidic.
Sedge Peat Moss
This type is harvested from sedge bogs. It has a low water-holding capacity and is less acidic than sphagnum peat moss.
Wood-based Peat Moss
This type is made from wood fibers and is a good source of organic matter, but it has a lower water-holding capacity than sphagnum peat moss.
Properties of peat moss

Peat moss is a unique organic material that has several properties that make it valuable in gardening, horticulture, and agriculture. Some of the key properties include:
Water-Holding Capacity
It has a high water-holding capacity, which makes it an excellent material for retaining moisture in soil. This property is particularly useful in dry or arid regions where water conservation is critical.
Acidity
It is acidic in nature, with a pH level ranging from 3.5 to 4.5. This property makes it a good soil amendment for acid-loving plants like blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons.
Nutrient Content
It contains several essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are important for plant growth and development. It is also rich in micronutrients like iron, manganese, and copper.
Aeration
It has a light and fluffy texture, which helps to improve soil aeration. This property is important for the development of healthy roots and the prevention of soil compaction.
Organic Matter
It is an excellent source of organic matter, which helps to improve soil structure, increase water retention, and promote beneficial microorganisms in the soil.
Sterility
Peat moss is generally free from weeds, pests, and diseases, which makes it a popular choice for starting seeds and propagating cuttings.
The environmental impact of peat moss harvesting
Peat moss is an important natural resource used extensively in the horticultural industry. It is harvested from peatlands, which are unique wetland ecosystems that store large amounts of carbon and provide important habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species. However, peat moss harvesting can have significant environmental impacts, particularly on peatland ecosystems.
Here are some of the main environmental impacts of peat moss harvesting:
Carbon loss
Peatlands are important carbon sinks, storing more carbon than all other vegetation types combined. When it is harvested, it releases stored carbon into the atmosphere, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
Habitat loss
Peatlands are home to a wide range of plant and animal species, many of which are adapted to the unique environmental conditions found in these wetland ecosystems. Peat moss harvesting can destroy or alter these habitats, reducing biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Water quality impacts
Peatlands play an important role in regulating water quality and quantity by storing and releasing water slowly over time. When it is harvested, it can disrupt the hydrology of peatlands, affecting water quality downstream.
Landscape disturbance
Peatlands are often remote and undisturbed areas, but peat moss harvesting can result in significant landscape disturbance, including the creation of large open pits, altered drainage patterns, and soil erosion.
Cultural impacts
Peatlands have been an important cultural resource for many Indigenous communities around the world. Peat moss harvesting can have negative impacts on traditional land use practices and cultural heritage.
The benefits of using peat moss in gardening
It is a popular and widely used material in gardening due to its numerous benefits. Some of the benefits of using peat moss in gardening are:
Water retention
It has the ability to retain water, making it an ideal medium for plants that require consistent moisture levels. This helps to reduce the need for frequent watering and conserves water.
Aeration
It is also able to hold air, which promotes root growth and prevents waterlogging of the soil. This is particularly important for plants that require well-drained soil.
pH balance
It has a slightly acidic pH, which can help to balance the soil pH for plants that require acidic soil conditions, such as blueberries and azaleas.
Nutrient retention
It can also retain nutrients and slowly release them over time, providing a steady supply of nutrients for plants.
Weed control
It can help to suppress weed growth by providing a barrier between weed seeds and the soil surface.
Disease control
It has antimicrobial properties that can help to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi in the soil, reducing the risk of plant diseases.
Sustainable alternative
Peat moss is a renewable resource that can be harvested sustainably and is biodegradable, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic growing media.
Alternatives to peat moss
There are several alternative materials to it that can be used in gardening and horticulture. Here are some of the most commonly used alternatives:
Coconut coir
Coconut coir is a natural fiber derived from the husk of coconut shells. It has similar water retention and aeration properties as peat moss and is a sustainable alternative as it is a byproduct of coconut production.
Compost
Compost is a nutrient-rich soil amendment made from organic matter, such as food waste, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials. It can improve soil structure, fertility, and water-holding capacity.
Leaf mold
Leaf mold is a type of compost made from decomposed leaves. It has similar water retention properties to peat moss and can improve soil structure and fertility.
Bark chips
Bark chips are made from shredded tree bark and can be used as a soil amendment to improve aeration and water drainage.
Perlite
Perlite is a type of volcanic glass that has been heated and expanded. It is lightweight, porous, and can be used to improve soil drainage and aeration.
Vermiculite
Vermiculite is a mineral that is heated and expanded to create a lightweight, porous material that can improve soil aeration and water retention.
Conclusion
This is a versatile and valuable material in gardening and horticulture. It has the ability to improve soil structure, retain moisture, and enhance nutrient uptake in plants.
However, it is important to be mindful of the environmental impact of peat moss extraction, as it can contribute to the depletion of important natural resources and release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
As gardeners, we can make more sustainable choices by using alternatives to it, such as coconut coir or compost, or by purchasing this that has been sustainably sourced and harvested. By making conscious decisions about our use of peat moss, we can support a healthier planet for ourselves and future generations.
You may also like to read
Discover the Top Plant Nutrients You Need for Thriving Plants






